|
|
0 comments
 Research Highlights:
Research Highlights:
- UNet++, a new, more potent architecture for medical picture segmentation, was unveiled by researchers at Arizona State University. Their design resembles a deeply-supervised encoder-decoder network, with dense, stacked skip routes connecting the encoder and decoder sub-networks. The semantic gap between the feature maps of the encoder and decoder sub-networks is intended to be closed by the newly developed skip paths. They contend that when the feature mappings from the decoder and encoder networks are semantically comparable, the optimizer would deal with a simpler learning task. Multiple medical image segmentation tasks, including nodle segmentation in low-dose chest CT scans, nuclei segmentation in microscope images, liver segmentation in abdominal CT scans, and polyp segmentation in colonoscopy recordings, were used to compare UNet++ to U-Net and broad U-Net designs. Their investigations reveal that UNet++ with deep supervision produces an average IoU gain of 3.9 and 3.4 points over U-Net and broad U-Net, respectively.
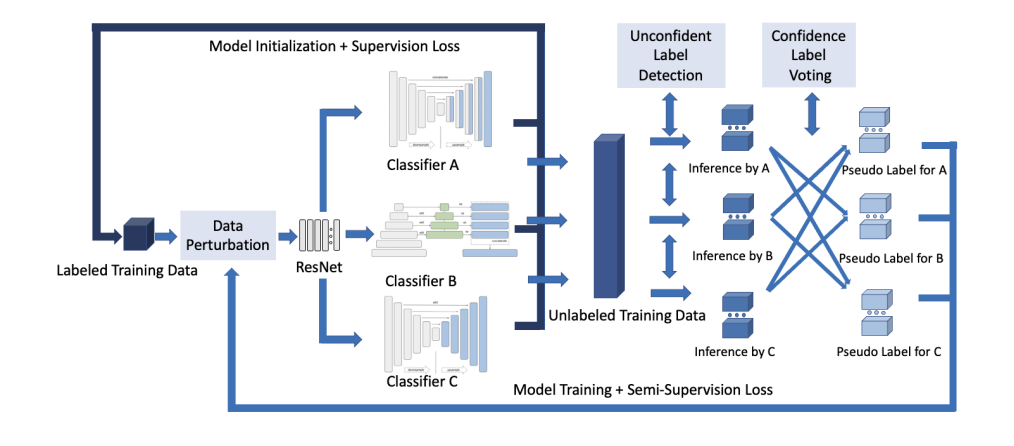
- TriSegNet is a semisupervised semantic segmentation framework that was proposed by Oxford researchers. On a sizable amount of unlabeled data and a small amount of labeled data, it employs triple-view feature learning. The triple-view architecture consists of three pixel-level classifiers and a low-level shared-weight learning module. Labeled data are used to initialize the model. Label processing, comprising data perturbation, cofidence label voting and unconfident label detection for annotation, enables the model to learn on labelled and unlabeled data simultaneously. The other two views of feature learning increase the confidence of each model. Four publicly accessible benchmark datasets, comprising ultrasound, CT, MRI, and histology pictures, are used to evaluate the segmentation findings.
Open Source Highlights:

- The ecosystems of NuGet, PyPi, and npm are the focus of a recent campaign that has seen over 144,000 packages released by unidentified threat actors. Researchers from Checkmarx and Illustria wrote in a paper released on Wednesday, "The packages were part of a new attack vector, with attackers spamming the open-source ecosystem with packages carrying links to phishing campaigns."136,258 of the 144,294 phishing-related packages that were found were available on NuGet, 7,824 were available on PyPi, and 212 were available on npm. The offending libraries have since been removed off the list or delisted. Further investigation has shown that the entire procedure was automated, the packages were uploaded quickly, and the bulk of the usernames adhered to the standard "a-z>1900-2022>." To deceive people into downloading them, the bogus packages themselves promised to offer hackers, cheats, and free resources. The package description contained links that led to the malicious phishing pages.

- B2B payments network CoreChain Technologies has partnered with open source software firm Odoo. According to a news statement issued by the firms on Thursday, December 15, this partnership would integrate CoreChain Technologies' embedded B2B payments and finance to Odoo's open source all-in-one business software and its ecosystem of 8 million customers.