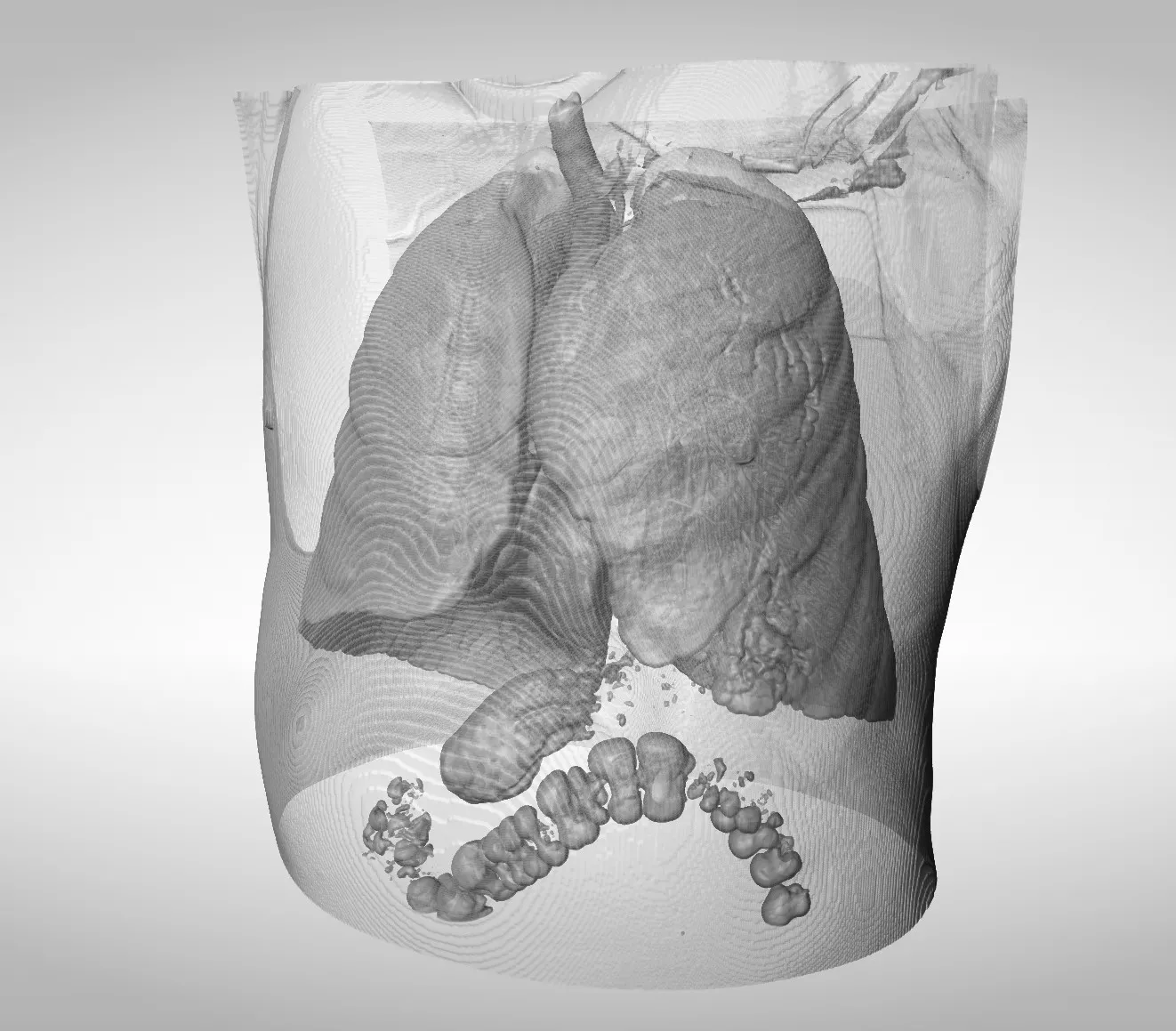
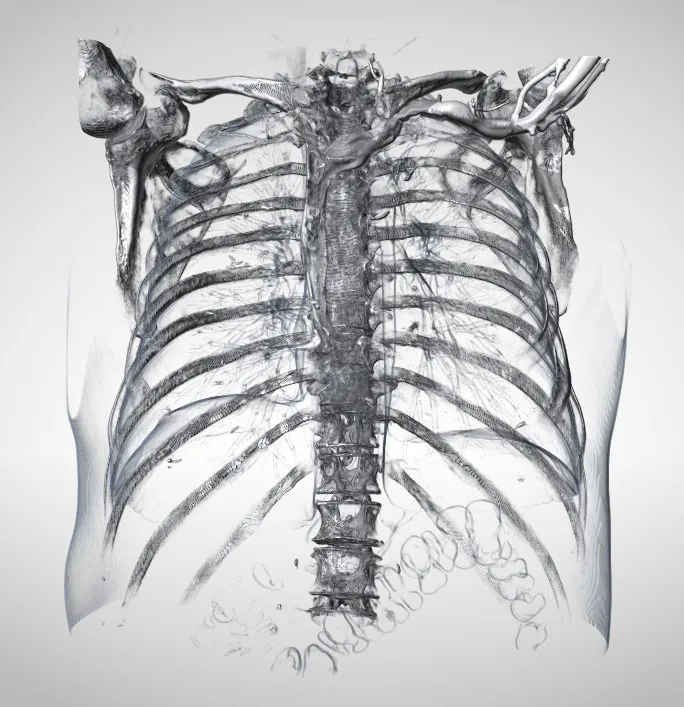
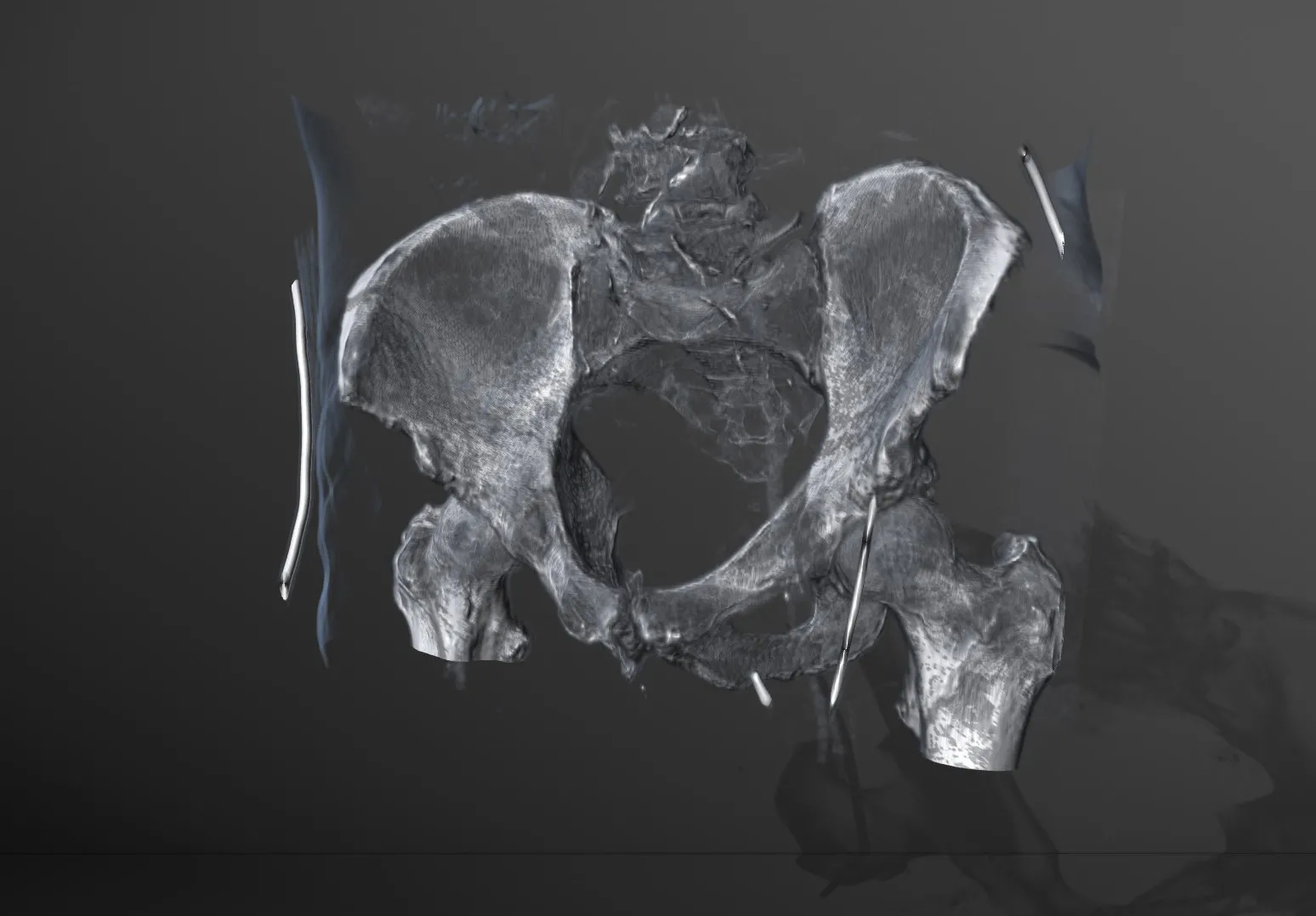
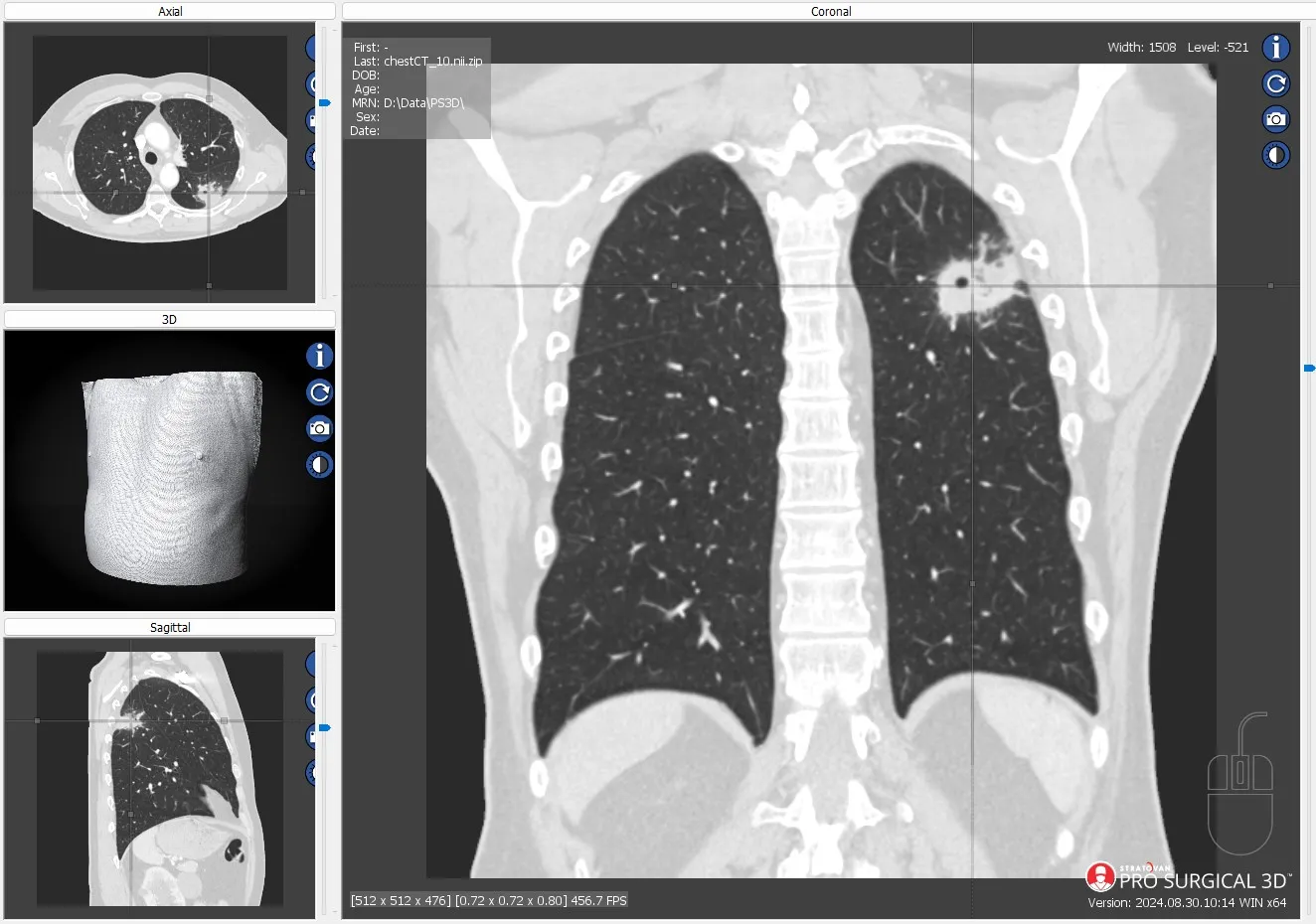
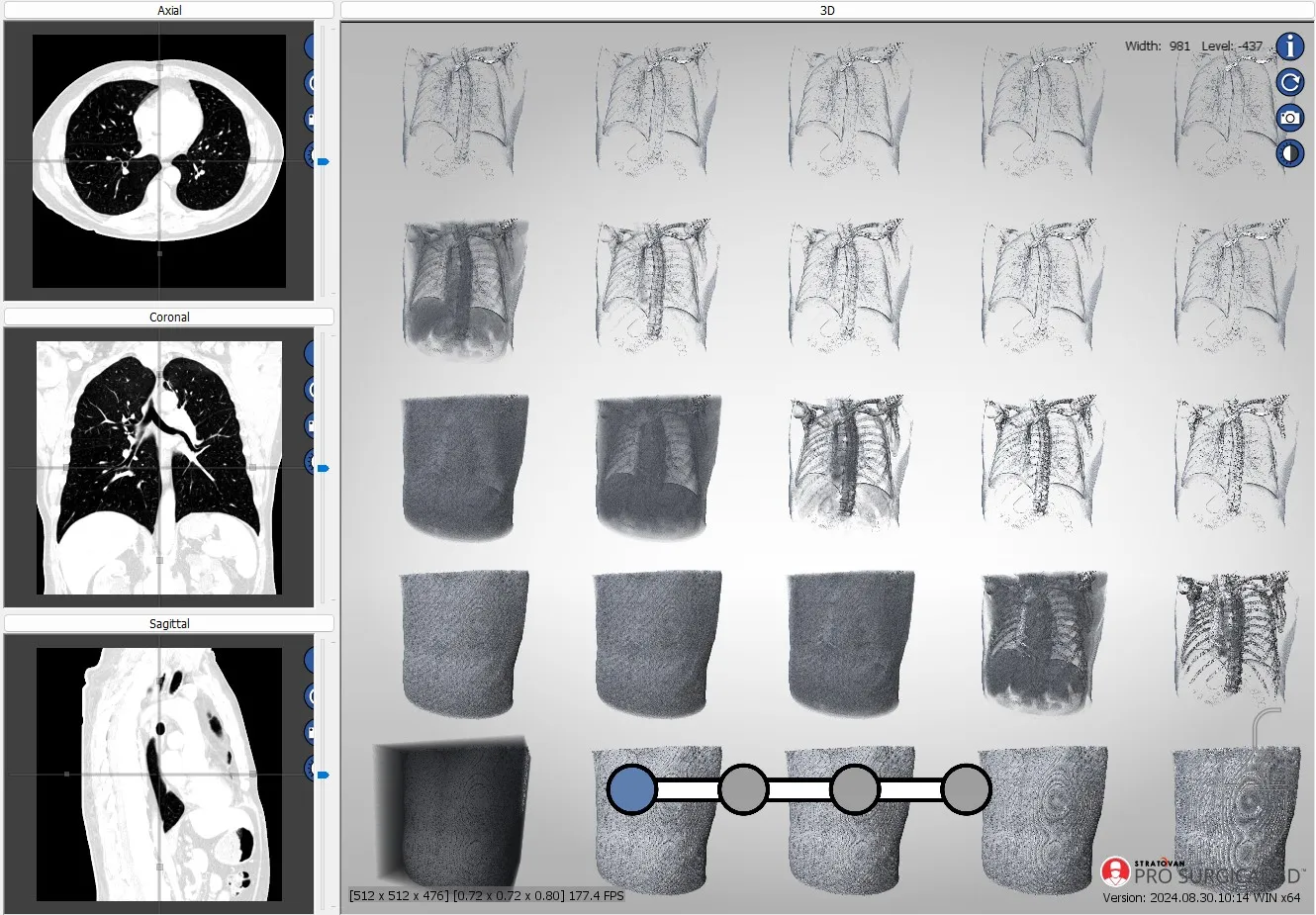
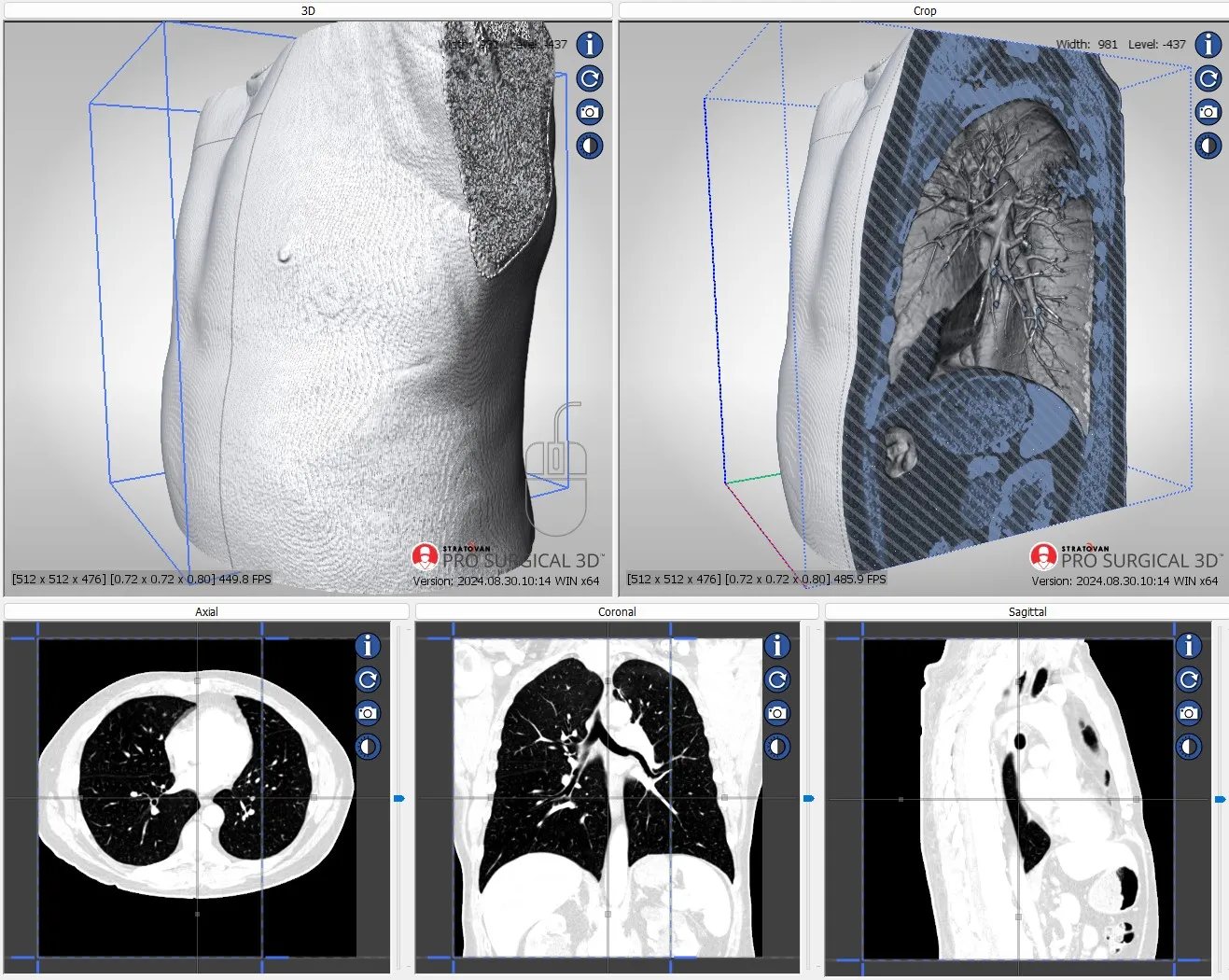
Pro Surgical 3D - view x-ray CT & MRI scans fast, efficiently & easily
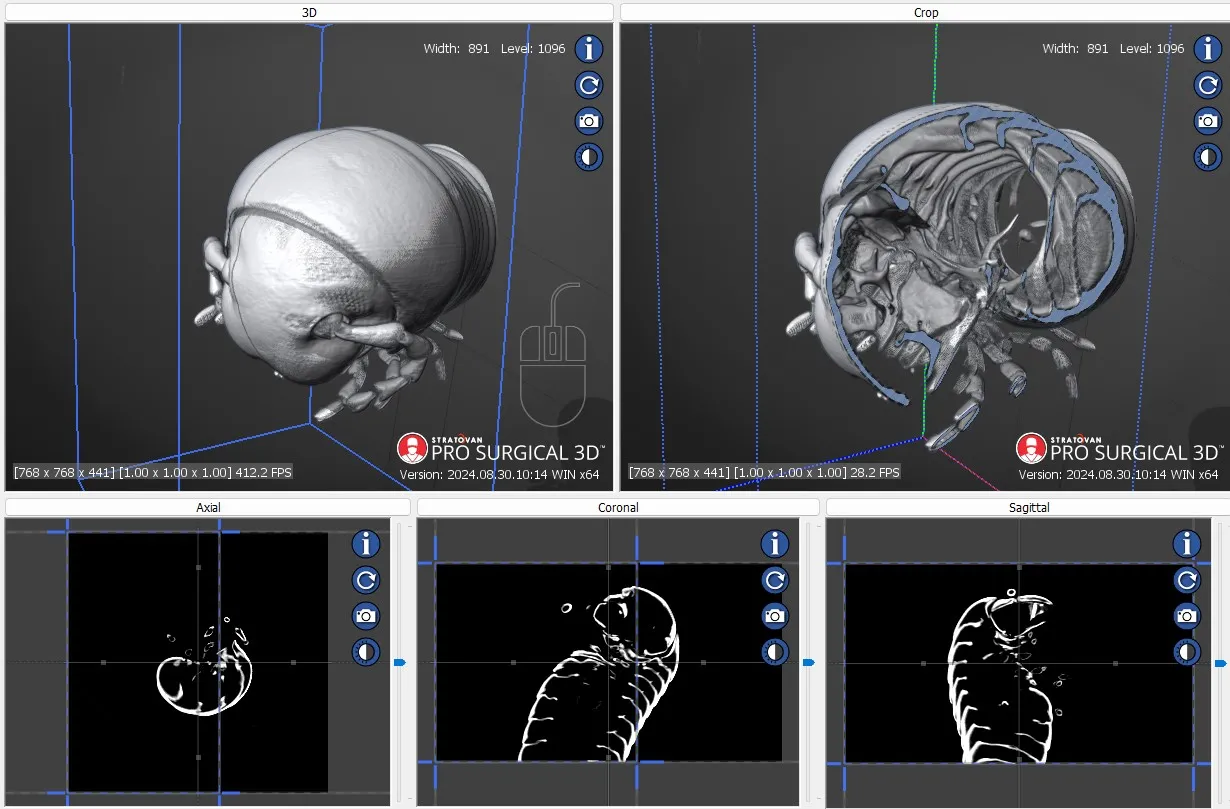
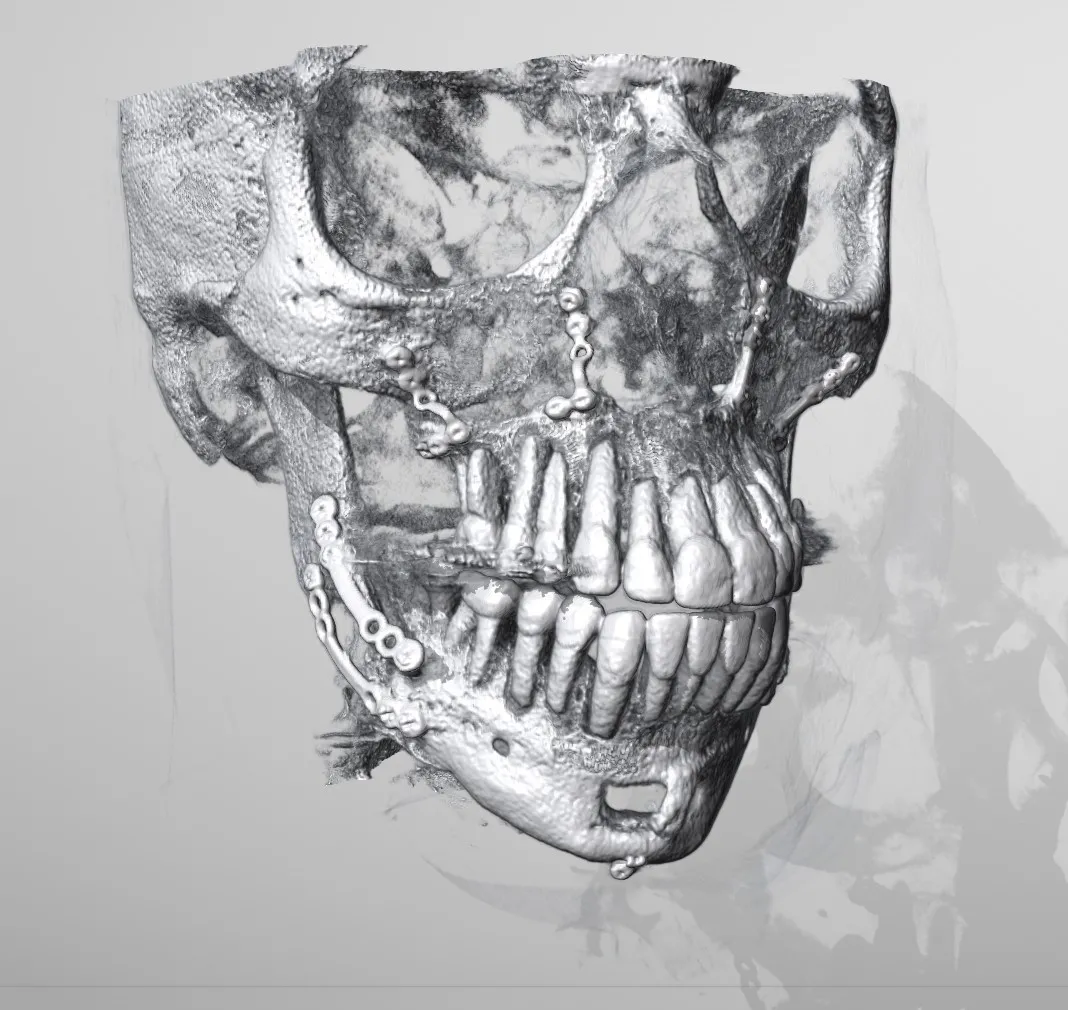
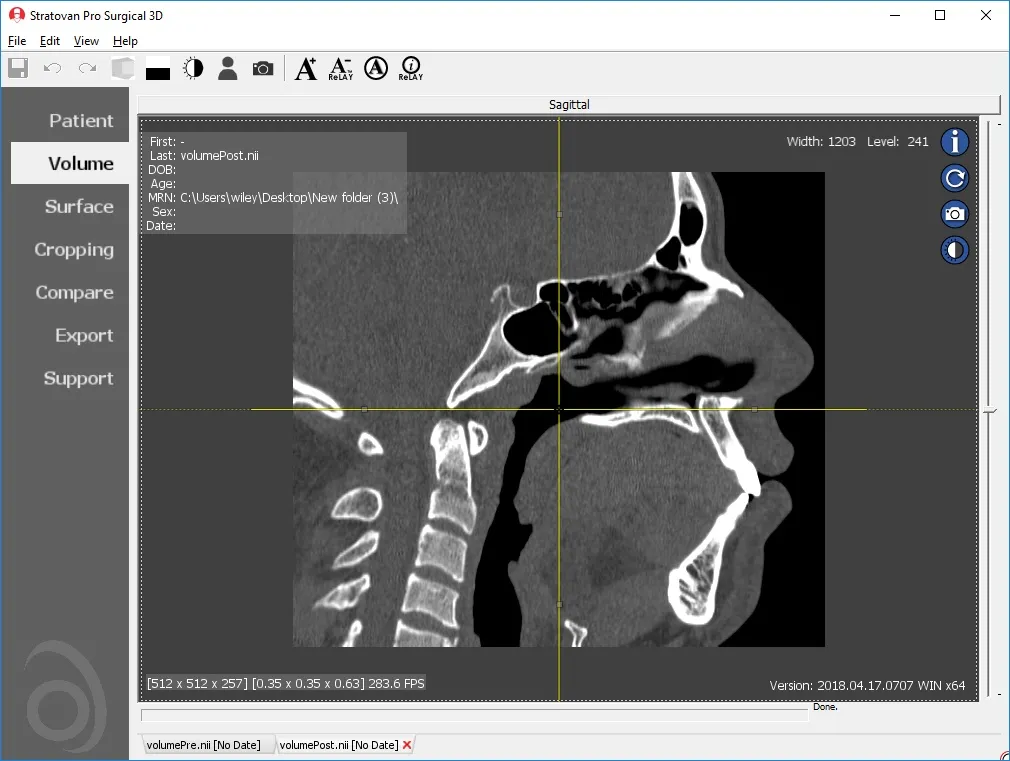
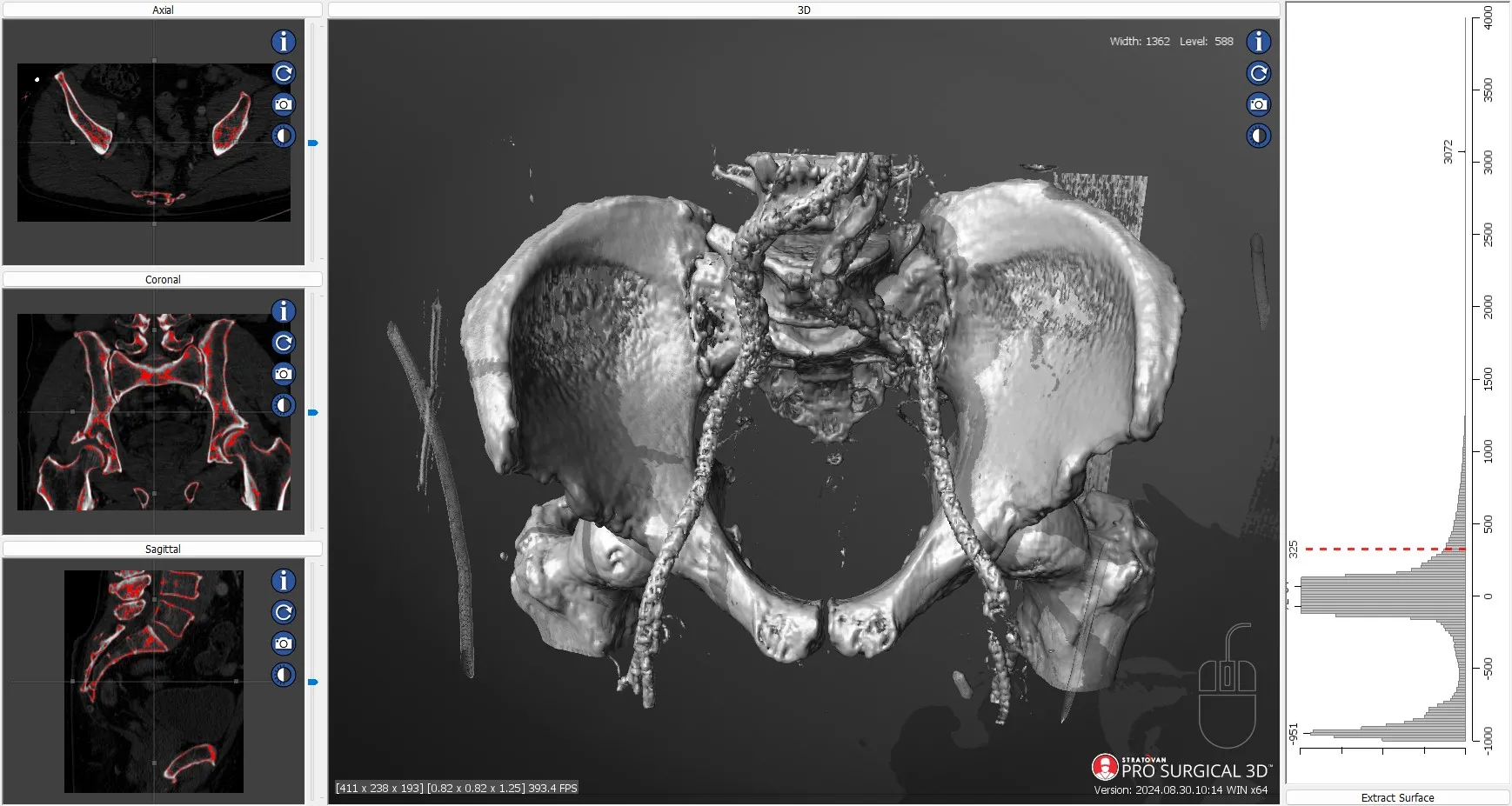
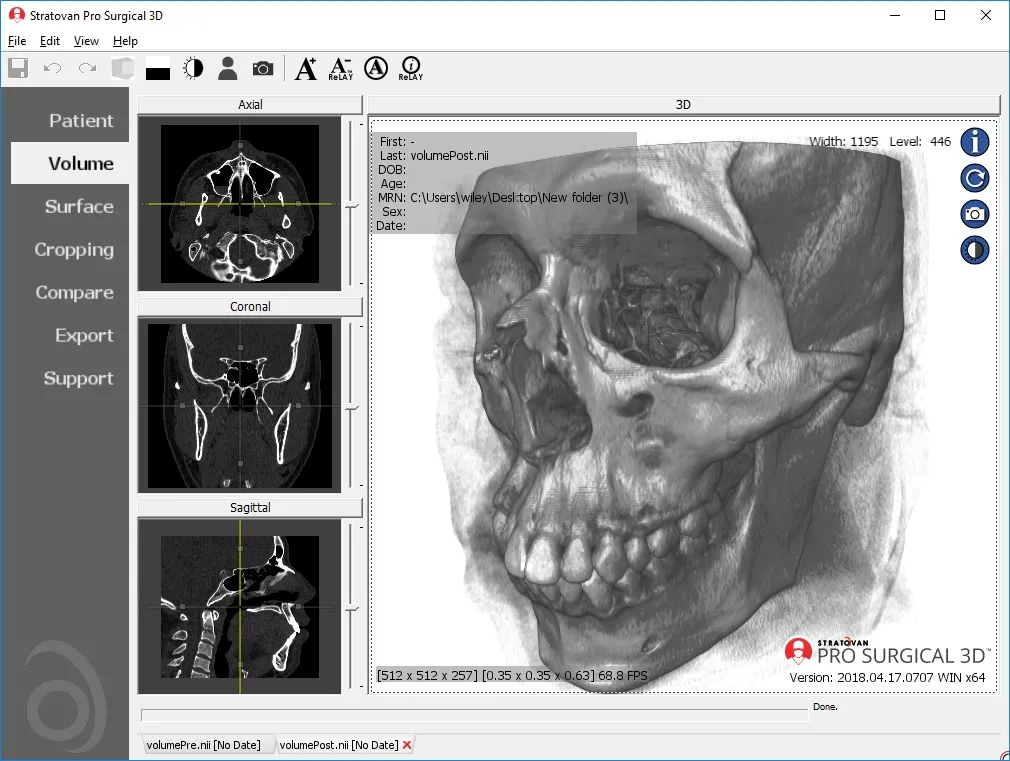
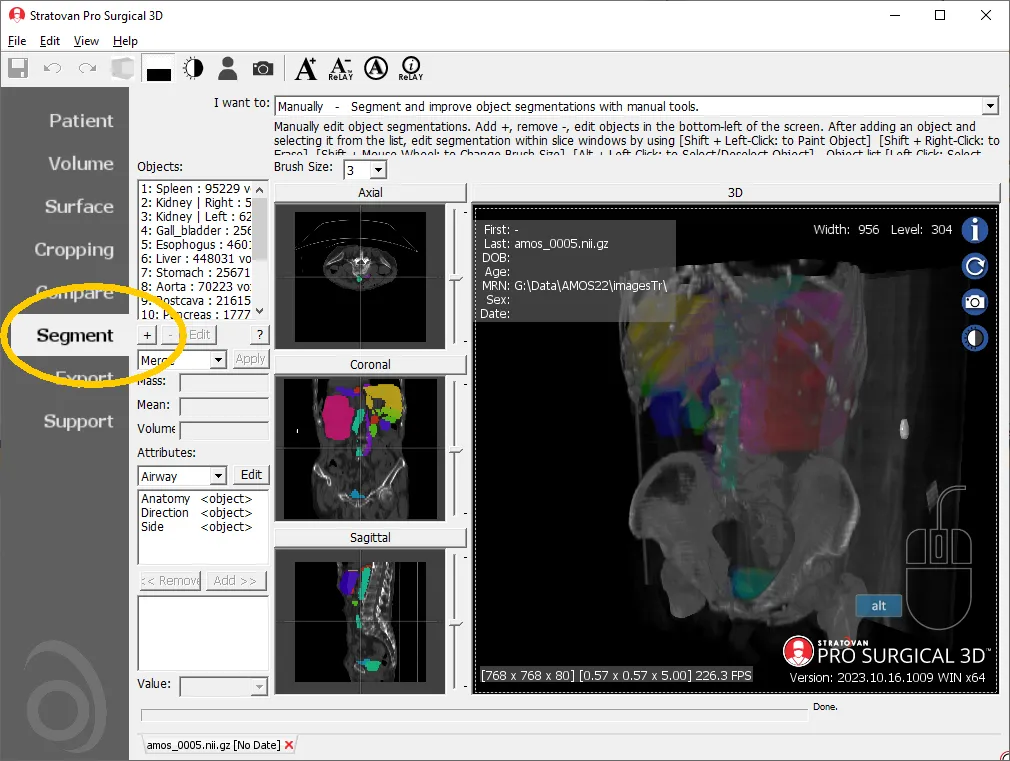
Pro Surgical 3D is a free and easy to use 3D DICOM Viewer – for surgeons and patient education. Designed for surgeons, Pro Surgical 3D makes it easy to view patient scans quickly. Pro Surgical 3D facilitates the optimal 3D treatment and assessment workflows based on X-ray CT and MRI scans – and best of all, it’s FREE!