Research:
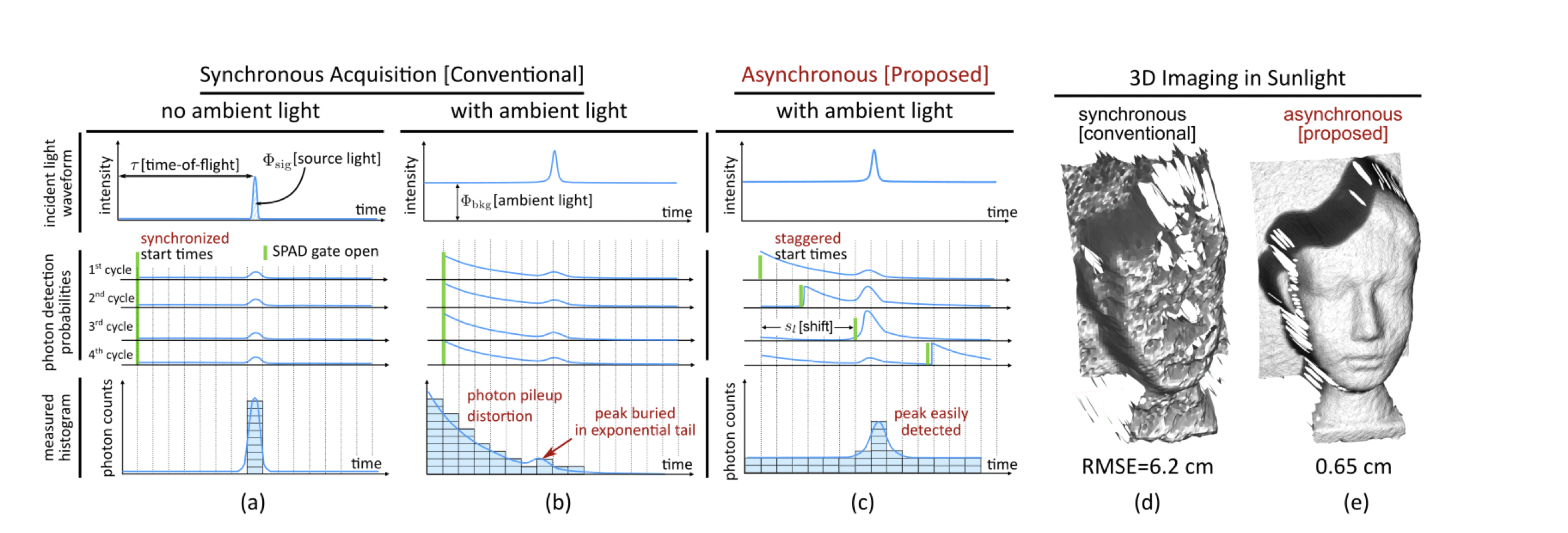
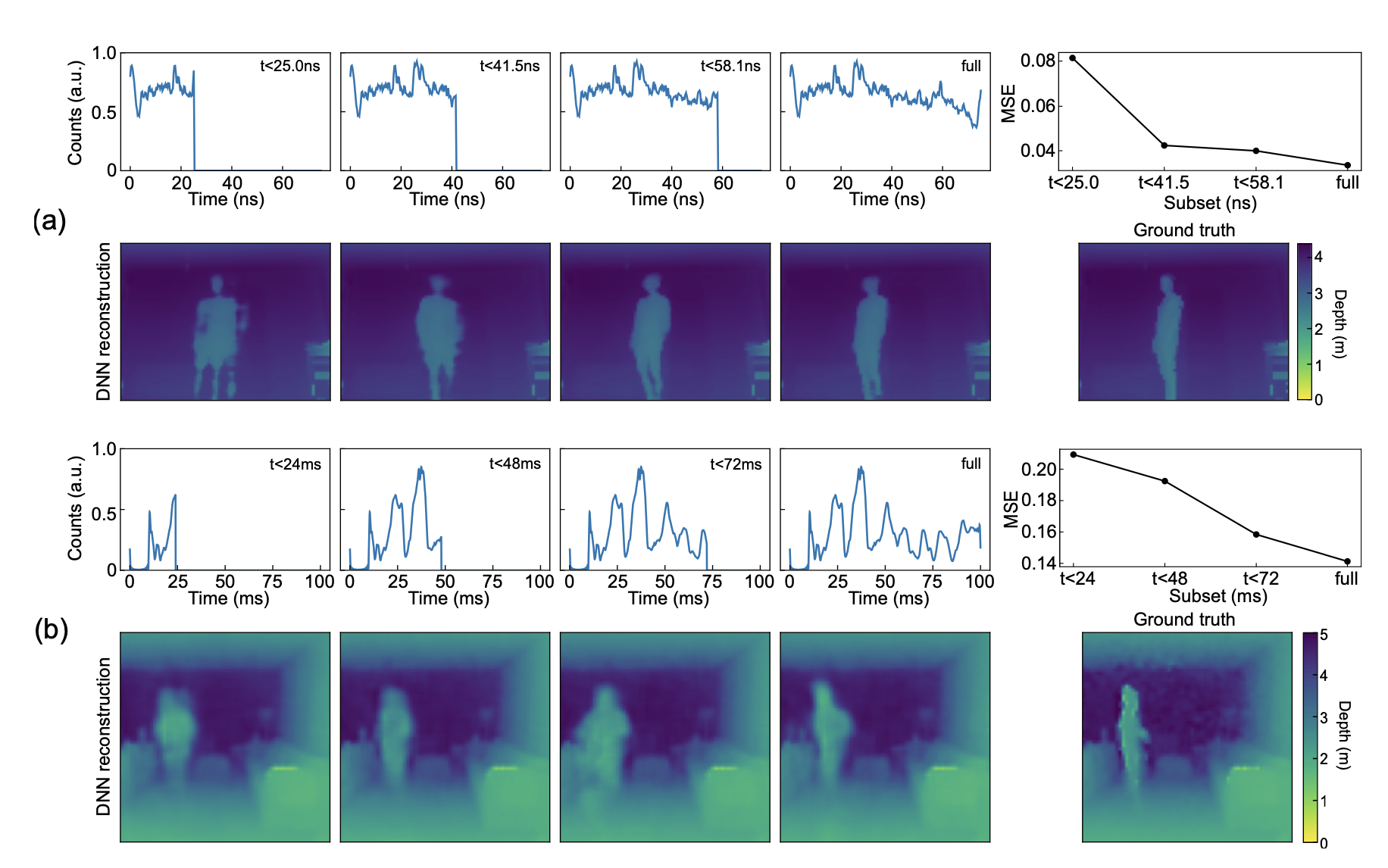
A family of data collection systems called asynchronous single-photon 3D imaging was introduced by University of Wisconsin–Madison researchers as a way to reduce data pileup during data capture. The laser cycles between deterministically specified or randomized offsets when acquisition is asynchronous, misaligning the timing of SPAD measurement windows. The main finding is that pileup distortions can be "averaged out" by selecting a series of offsets that cover the whole depth range. Their models and experiments show that, compared to the state-of-the-art, a number of imaging scenarios, including those with high ambient flux, can be captured with depth accuracy that is up to an order of magnitude better.
The term "echo-location" refers to a comprehensive approach of imaging and sensing that incorporates both animal navigation and man-made RADAR, LIDAR, and SONAR. However, in order to provide the spatial location of the echo origin-points, complete 3D information based on echolocation necessitates some kind of scanning of the scene. Without this spatial information, it is extremely difficult to image objects in three dimensions since the inverse retrieval issue is severely ill-posed. Researchers from the University of Glasgow demonstrated that the temporal information included in the return echoes that are reflected more than once inside a picture is sufficient to accurately depict an image in three dimensions. By visualizing people moving in a contained space utilizing both radio-frequency and acoustic waves, they experimentally proved the concept.
Open Source News:

There is a challenge to maintain transparency in the development of proprietary large language models (LLMs), particularly in regulated industries. OpenAI, Microsoft, and GitHub are facing lawsuits over their coding assistant, Copilot, and there are concerns about personal information use that led to the temporary ban of ChatGPT in Italy. To address these issues, Big Code, an open science collaboration, has released an open source LLM called StarCoder. StarCoder is not only trained on code but also on GitHub commits and issues, making it useful for answering coding-related questions and acting as a tech assistant. The Big Code team has created an alpha version of a chatbot called StarChat. The model has been trained on a large dataset called The Stack, consisting of source code in over 300 languages, and further trained on the Python subset to create StarCoder.

The popular open-source large language model LLaMA from Meta was leaked in March, according to a letter from two U.S. senators to CEO Mark Zuckerberg on Tuesday. Experts warn this poses a threat to the open-source AI community. It is noteworthy because it occurs at a crucial time when Congress has made regulating artificial intelligence a top priority and while open-source AI is experiencing a surge in new LLMs. Blumenthal and Hawley wrote Zuckerberg's letter on behalf of the same subcommittee. The senators expressed alarm over the "potential for its misuse in spam, fraud, malware, privacy violations, harassment, and other wrongdoing and harms."